
What is cold welding, and how does a cold welding machine work?
The joining of the metal with little or no heat is cold welding. It is an interesting method of welding where physics and an understanding of material science work.
Here we will be learning what is cold welding and how does it work and what metals can we weld?
How to define cold welding?
The process of cold welding needs no heat input to join the metal workpieces together. The metal is not molten at any stage and remains in a solid state. Thus cold welding is labeled as a solid-state welding process. The necessary energy to join the metal is applied in the shape of pressure. Cold welding never has the metal in a molten state as compared to fusion welding or arc and friction welding.
The pressure application brings the metal surfaces as close as possible. The extent of pressure makes the nano distance irrelevant, the atoms from the metal jump from one sample to another. This leads to a near-perfect joint with no consequences, and two metal pieces become a homogenous bunch.
To acquire this result we need a very clean metal surface near to perfection. As every metal is having an oxide layer that needs to be removed before the commencement of the cold welding. We will discuss this in more detail but let us first understand the pros and cons of the process.

Advantages of cold welding
✦ It is a perfect way to weld aluminum.
✦ Aluminum and copper joining is a perfect advantage in cold welding.
✦ No heat-affected zone and concentrated heat zone of arc welding are absent here.
✦ Near-perfect welding joint without any intermetallic brittle compound, microfractures, and other defects.
✦ Join dissimilar metals, that are difficult to weld otherwise.
✦ Can weld exotic metals like copper, gold, etc.
✦ The skilled power is reduced.
Disadvantages of cold welding
✦ Thorough cleaning of the surfaces is required.
✦ Need multiple, cumbersome, cleaning, and preparing steps.
✦ Contamination, irregular surfaces and nanoscale structures can hamper the results.
✦ A non-starter for industrial setup due to aerial dust and debris.
✦ Not fit to weld carbon steel and hard metal, only works for nonferrous metals like copper, aluminum, lead, gold, etc.
✦ Not suitable for irregular surfaces and can give the best result with flat surfaces only.
What are the uses of cold welding?
This welding process is used in many industries that including aerospace, electronics, and automotive production. The cases where dissimilar metal wires are required to join are the best suited of all welding processes.
Cold welding is best-suited for inlaying underground wire when there is a danger of fire eruption of flammable gasses during the fusion welding process.
This is a perfect solution for the sealing of containers with explosives, which are heat sensitive otherwise. It is opined that cold welding is employed where heat may cause more damage or be liable to the danger of heat.
How does cold welding work?
This welding process joins metal at an environmental temperature without any heat and flow of electrical current in the joint. Application of the force to the metal samples removes surface roughness and resolves irregularities on the surfaces. But the prime reason to apply pressure is to enhance interatomic attraction between the metal surfaces.
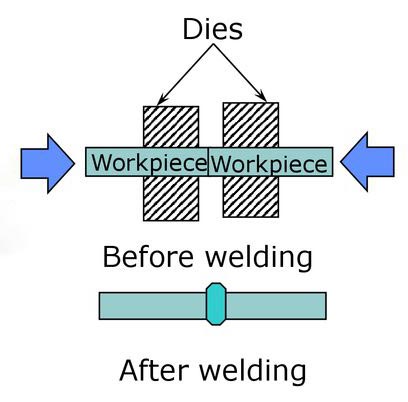
To initiate cold welding, the removal of the oxide layers from both metals is essential. Every metal is bound to develop an oxide layer on the surface, which makes the inner metal pure and inaccessible. The pressing of the two oxidized, unclean copper pieces will fail to achieve a weld.
After cleaning the surfaces thoroughly, when applying enough pressure, the metal turns to a uniform metallurgical bond. The newly formed metal acts as a homogenous piece near to base metal. This needs extraordinary cleanliness and absent surface irregularities.
This level of uniformity can mainly be achieved with welding wires only because the cold wire welding process drains out impurities with almost perfection and precision.
Essentials for cold welding
The pristine cleaning of metal surfaces and accurate joint geometry are the main prerequisites. Clean and flat joint surfaces are mandatory making flat and irregular free shapes desirable. The oxide layer and impurities tend to be removed by degreasing, wire brushing, chemicals, etc.
Oil and grease on the metal surfaces must be removed before cleaning with a wire brush. This process is essential otherwise brush can push these impurities deeper into the metals.
Once we clean the oils, we can proceed to clean away the oxide layer. Different bristle materials and brush types may be recommended depending on the specification of the metal.
Is cold welding strong enough?
Definitely, the cold welded joint is as strong as the parent metal if done properly after necessary preparation. The cold-welded joint strength relies on the properties of the metal. Cold welding can not outperform the original metal strength as in other fusion welding methods.
The joint strength will be jeopardized if the cleaning of surfaces is insufficient and irregular. In situations like cold welding applications as in joining wire, a stable bond can be achieved easily.
Weld joint possibility
By virtue the cold welding pressure works better with a big contact surface, so is best to use it for butt and lap joints. Joining of welding wire and pipe are butt welds because it is easy to trim the ends, secure clean metal, and press the wires together.
In the case of butt weld, the gap between the clamping points and contact surface need not be big as soft metals may bend sideways instead of connecting.
The lap joint is tricky to achieve in cold welding. The metal sheets pressing together will decrease the thickness due to pressure. There may be a loss of up to 50% thickness when calculating for the project. Otherwise final material will not fit into project requirements.
Even if our weld is perfect, the thinned part can not be unacceptable. Calculate the resultant thickness considering metal ductility and softness.
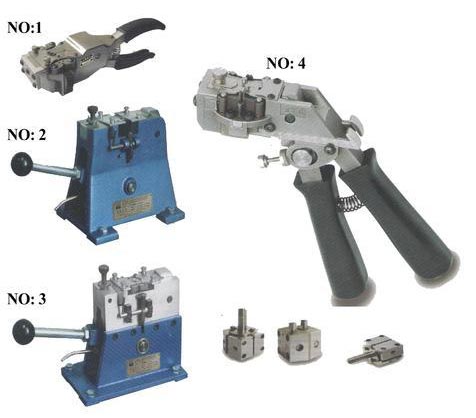
Cold welding machine to join wire
Cold welding machines for small wire diameters are generally hand-operated equipment. Larger diameter metals may need a pneumatic or electro-pneumatic technique. Most of these machines which handle wire, strips, and rods are portable.
Pneumatic intensifier usage in portable cold welding machines will generate intense pressure. There is a welding head on the operator’s side. The operating head is placed at the top of the machine and acts to take it as a welding die, control the applied pressure, and maintain stability.

Once the die is placed and secured in the die pocket wires or rods are fed in on the sides. The pressure application makes the die crimp the wire near endpoints and push tightly together. The pressure here squeezed out the impurities from their cores outwards. This way cold welding wire creates a better joint than sheet metal welding. This is due to small joining surfaces in the wires, unlike sheets.
Application of pressure is a minimum of 4 times to squeeze out all the impurities. The process is defined as a multi-upset principle. Once the wires have bonded, we can remove them from the machine and chip away residue around the joint area.
Hot welding vs cold welding
The hot welding process includes steps such as an electrical arc, resistance, active flame, melting, and fusing of the metal. Cold welding is fusion by pressure and is best suited for nonferrous metals.
Features of Hot welding
✦ Requires heat
✦ Need an electric arc
✦ No pressure is required
✦ Can weld almost all metals
✦ Wider application in industries
Features of cold welding
✦ No need for heat
✦ No need for an electric arc
✦ High pressure is required
✦ Can weld only non-ferrous carbon-free
✦ Limited application
What can and what can not be cold-welded?
The list of metals that can be cold-welded includes aluminum, copper, lead, zinc, brass alloy, silver, nickel, platinum, silver alloy, and gold. It can weld aluminum alloy series 2xxx and 7xxx which is otherwise not possible.
Cold welding is best suited to welding metals that have a face-centered cubic arrangement of atoms and do not harden quickly. The ductile metals are the fit choice to be cold-welded as outlined in the above list.
It is not possible to weld carbon steel, an alloy that contains carbon. As carbon steel is by far the most welded metal, so cold welding application is limited.
Types of cold welding
Cold welding does not have different types. There are similarly named methods mistaken for cold welding. It is time to have a look at these methods to understand them.
1. TIG cold welding
This method has no relation to cold welding. Some of the TIG welding machines have a cold setting that limits the heat input. It can be achieved by applying a tiny arc spot for fraction of a second.
The temperature here remains minimal as generated heat dissipates hurriedly with a metal of high conductivity in metal like aluminum. This is a useful technique for joining very thin sheets of metal & wire. Similar results can be achieved with TIG welders using the pulse settings.
We can get low-heat TIG welding by setting a very low pulse current and high time between the pulses but cold welding is a better choice.
Cold welding vs TIG welding
2. Cold metal transfer
In cold metal transfer, an arc is employed to create a joint as fusion welding. This is a misnomer and mislabeled as cold welding and creating confusion. This is a MIG welding process that needs 90% less heat input instead of a regular process of MIG welding.
The cold metal transfer method is so cold and solves many problems of actual cold welding techniques. We should be careful in defining two techniques.
The present process of CMT utilizes an electrical arc, and filler metal, and can be a useful tool where cold-pressure welding is not an option. The CMT needs precision in the selection of filler wire to control the heat input.
3. J B Weld

This JB Weld is a brand name from the group of epoxy bonding systems for fiberglass, metal, concrete, bricks, etc. It may be called the original cold weld formula but it really does not make a weld between the metals.
Here the two metals do not fuse to change to a homogenous mass by interatomic attraction as in the cold welding process. The metal pieces just adhere, but not be welded together. This JB Weld is epoxy with a base and activator as two components. We mix and apply over the metal ends, secure them with clamps, and start the curing.
This provides a weak bond with a strength of 5020 PSI as compared to the E6010 electrode.
It is not cold welding but a process where small repair in a house is possible.
Which metals can be cold-welded?
The metals which are very ductile can be cold-welded. This technique is very useful to join aluminum, especially grades like the 7XX series which are otherwise unweldable. The brass alloy in 70/30, zinc, copper, nickel, silver, silver alloys, and gold, as wires.
Cold welding can join metals such as stainless steel, after applying great pressure. Carbon-containing metals can not be cold-welded.
Does cold welding have enough strength?
With inaccurate preparations and conditions, cold welding can produce a weld as strong as the parent metals. Needful for this welding the metals should be ductile, regular surface, clean of oxides, and smooth.
Despite the mentioned factors, cold welding has the capability to create the strongest possible welds.
Does cold welding create a permanent weld?
Under the right and favorable circumstances, cold welding can produce a permanent weld. If done correctly the cold welded joint is permanent and reversal can damage the workpiece.
The strength of the joint depends upon the preparation, if not done properly, the joint may fail.
A unique bonding technique that can create strong bonds without use of the heat is called cold welding.
The cold welding history dates back to the bronze age around 700 BC but was in its primitive stage. The first documented scientific experiment was conducted in 1724 by Reverend J.I. He pressed 2 lead balls together to form a solid joint.
If challenges are overcome timely, cold welding can produce a strong bond between dissimilar metals and some of the non-weldable aluminum grades even.
It can be a useful option for joining wires, aerospace, and automotive industries
Thank you for sparing a little time to read the stuff.
Remember, though, that you can always take it to the next level with additional reading material 📚
Similar Posts:
12 Different Types Of Welding Processes [The Definitive Guide]
Cast Iron Welding Procedure [Step-By-Step Guide]
References…
