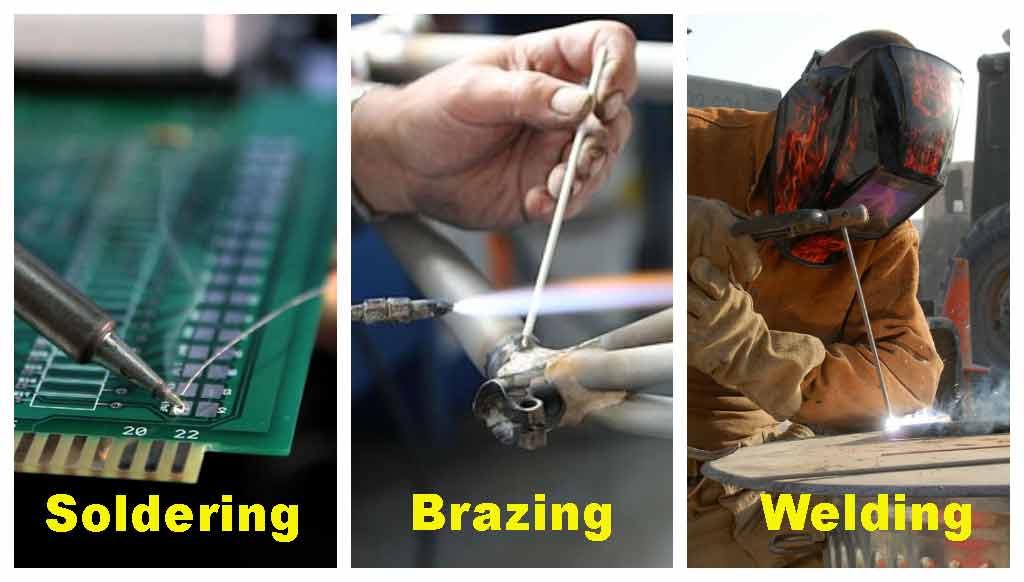
The Difference between Soldering and Brazing with Welding [The Definitive Guide]
You have a situation to join two materials together, in a few cases glue and cement can work. Rivets, staples, and nails even can create pretty secure bonds. However, the situation will be different if you are to join two metals.
Let me explain the difference between soldering and brazing with welding.
We need techniques like soldering, brazing, and welding where heating of the metal is the principle. These three methods intermingle and confuse users.
They have many features alike but serve different metals and their applications. Every process needs different equipment, skills, and gears.
Comparison of Welding, Soldering and Brazing.
| Sl.No. | Welding | Soldering | Brazing |
| 1 | These are the strongest joints that can bear the load. The strength of the welded joint can exceed the strength of the base metal. | These are the weakest joint of the three. Not to bear the weight. Generally, use to make electrical contacts. | These are stronger than soldering but also weaker than welding. It can be used to bear some load. |
| 2 | The temperature of the desired welding zone is upto 3800°C. | Temperature required upto 450°C. | It may go up to 600°C in brazing. |
| 3 | The workpiece needs to be heated to their melting point to join. | Workpieces do not need to be heated. | The workpiece is heated but below the melting point. |
| 4 | The mechanical properties of the base metal may vary in the joint space due to heating and cooling. | There is no change in mechanical properties after joining. | The mechanical properties of the joint may change, but it is almost negligible. |
| 5 | Involving heat consumption, high-level skills are required. | The costs involved and the skill requirement is very low. | The costs involved and the skills needed are between the two others. |
| 6 | Heat treatment is usually required to eliminate the unwanted effects of welding. | No heat treatment is required. | No heat treatment is required after brazing. |
| 7 | Since it is performed at high temperature, it is not necessary to preheat the work before welding. | Preheating the workpiece before soldering is good for making good quality joints. | Preheating is beneficial for forming a solid joint because brazing is done at relatively low temperatures. |
Common Features of Welding, Soldering, and Brazing
Metal joining requires soldering, brazing, and welding. Each of these methods is different but has numerous things in common.
Cleaning – Most essential is the cleaning of metal pieces, whatever may be the process. Doing soldering, brazing, and welding on unclean metal pieces causes gas or liquid flow and structural defects.
Heated Material – All the three methods require heating either filler material, metal parts to be joined, or both. It requires sufficient heat to create a strong joint to serve the practical application.
Proper accessories – In brazing, soldering and welding operators require using safety gloves, protective clothes, helmets to save from a fire, projectiles slag, UV light. Operators need to cover skin, eyes, and very parts as safety measures.
Definition of soldering and its equipment

Definition – The soldering process joins two metals together when solder applies to metal pipe sections. The solder, a filler metal, gets melted by soldering iron at a low temperature up to 450 degrees centigrade. The solder may be solid in wire form, paste form as flux, laid right over the materials to be joined. I do the heating here to solder only not the workpieces. The difference between soldering and brazing is the amount of heat involved only.
The most common use of soldering is electrical contacts mainly but applied in plumbing and metalwork of low temperatures. We apply the method for metal like iron, gold, silver, copper, and brass.
Soldering Iron Kit

- Soldering iron
- Solder and flux
- Wire cutter
- Solder sucker
- Wet sponge
- Soldering stand
- Safety glasses
Soldering Technique
Soldering of iron is the simplest and oldest technique known where a soldering iron with copper tip stores and carries heat to the joint/seam. The soldering involves preparing the metal, heating the ends, pouring solder in the joint/seam, cooling, and cleaning the metal.
The electronic components and circuit board manufacturing require the use of wave soldering. The wave of solder moves continuously into contact with the metal joints and seams.
The speed of the process is very high and to maintain it we use an automated solder machine. This machine can preheat solder/flux and can remove the residual flux continuously. Soldering is a comparatively simple process with a moderate level of difficulty.
Pros of Soldering
1. No need to melt the base metal
2. Thin-walled parts and dissimilar materials joined together conveniently
3. Low-temperature process
4. Low-cost method
5. Easy to master this art
Cons of Soldering
1. Not fit to fuse large sections
2. Unfit for high temperature applications
3. Seams and joints are low in strength
4. Solder has toxic components
Definition of Brazing and its Equipment
Brazing
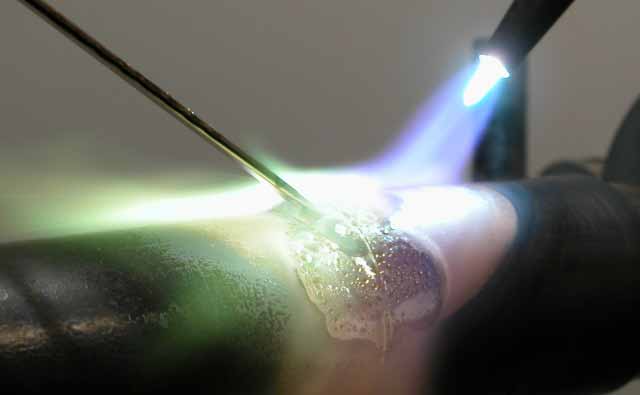
The brazing principle is the same as soldering where a combination of heat, filler material, and flux works to join the metals together. But in brazing, a flux solution between the filler metal and base metal is used to join in heating.
The difference between brazing and soldering is a temperature of 450 degrees centigrade used in brazing, which is much higher than soldering temperature. Unlike welding both soldering and brazing heat the filler metal sparing the base metal from melting and joins the two metals together.
Brazing is an adequate tool for very thin metal, like aluminum. Higher temperatures can damage these metals. It is also a handy tool for the joints, which are difficult to access on soldering. Most carbides, ferrous metals, and cermet can be fused by brazing.
Brazing Equipment
1. Furnace, torch, induction coil, the chemical bath heater for melting the filler material.
2. Filler material or flux solution, the commonest filler metals in brazing include chlorides, fluorides, borates, alkalis, and fluoroborate.
3. Safety gears for the brazing include thick cotton gloves, safety suits, and safety goggles.
4. Single-phase secure electricity supply.
Brazing Technique
The gas torch of brazing utilizes oxyfuel gas like propane, acetylene, and LPG as well. Time to put the involved parts with preloaded filler metals and the flux in the brazing furnace. The process commonly placed on automation in the industries.
The heated chemical bath of the fluxing agent and the heat source is called dip brazing. The dipping of preassembled parts and pre-set filler metal happens in the brazing bath. It quite suits the technique to the aluminum assemblies.
Start induction brazing by clamps holding the metal to be brazed to inductor coils. It creates an electrical current around preset flux, and pre-assembled and preloaded with filler metal.
The brazing is a useful process where the assembly would be adversely affected by excessive heat, but here allows heating selectively. Moderate skill is enough for the brazing.
Pros of Brazing
1. Base metal spared from melting.
2. Neat and clean joints with none cleaning.
3. It can join dissimilar metals and even non-metals.
4. The economical way to fuse the material with multi parts assemblies.
5. The technique is simple to follow.
Cons of Brazing
1. Larger sections are not possible to join.
2. Joint strength is not as strong as welding.
3. High temperature can damage the brazed/seamed joint
4. The color of seam/joint differs from base metal.
5. The filler material may contain toxic elements in it.
Definition of Welding and its Equipment
What is Welding?

The high temperature heats the filler material and edges of the base metal to establish a strong weld between the workpieces of metals.
The temperature over 450 degrees centigrade involves welding which is much higher than soldering and brazing. Unlike in soldering and brazing, it melts the base metal to make a powerful bond.
Welding process used commonly in industries and day to day life. The applications include construction, building, automotive, shipbuilding, aircraft, pipelines, tanks, vessels, heavy construction equipment, erecting bridges, and railroads. In one procedure, it uses thousands of welding joints.
There are several methods of welding such as TIG welding, MIG welding, Arc/stick welding, Gas welding, Laser welding, and underwater welding in marine applications.
What is TIG Welding?
Welding Equipment for Gas and Arc Welding
1. Fuel gas cylinder
2. Welding torch
3. Oxygen cylinder
4. Electricity source
5. MIG/TIG/Arc welding torch
6. Filler material
7. Spool of filler wire
8. Protective gears
9 Shielding gas
Welding Technique
The heated electrode or flame once applied to the margins of base metals, the edges melts which on cooling make a strong joint. The filler material may be used to fill the gap. The shielding gas is part of arc welding processes.
We consider this more difficult than soldering and brazing. The process has a complex procedure to master the skill. Extreme high temperatures need extra precaution of safety.
Please let me know if you are also looking for welding machine details.
Pros of Welding
- Different materials can also be welded.
- Strong and secure joints and seams.
- Welding can be done anywhere.
- Economical procedure.
- Generally neat, without residue.
- Larger sections joining.
Cons of Welding
- Harmful effects like radiation, toxic, burning, blinding light.
- Sometimes expensive.
- Generally not suitable for thin metals except in TIG welding.
- Base metal distortion and change of characters.
You Might Also Enjoy…
12 Different Types Of Welding Processes [The Definitive Guide]
Thermit Welding: Operation And Steps [With Set-Up Diagram]
Understanding The Welding Symbols [Explained With Diagrams]
Cast Iron Welding Procedure [Step-By-Step Guide]
Frequently Asked Questions
Soldering vs Brazing which is stronger?
The brazing if done properly can be stronger than the pieces to be joined, but not as strong as the welding joint. Brazing does not affect the base metals. Soldering is the lowest temperature technique to fuse the materials. The soldering can be done with metals like silver, gold, brass. and iron.
Soldering vs Welding which is stronger?
Proper soldered and brazed joints can be stronger than the base metal pieces, but are not as strong welded joints. Soldering is low-temperature analog to brazing but not strong as welding.
Brazing vs Soldering, differences between soldering and brazing.
Brazing being stronger than soldering, but there are no effects on the base material in soldering. The lowest temperature used for soldering and brazing. Brazing needs filler flux along the high temperature to join the parts.
Why is brazing better than welding?
The difference between welding and brazing is that welding can change the base metal structure and its composition while brazing does not affect the base material. The properly completed brazing offers a strong joint as welding does. Brazing is quite a handy tool for thin metal structure.
Why are bike frames brazed instead of welding?
The thinner metal of bike frames require brazing than welding. To maintain the base metal in proper shape the brazing is the choice instead of welding. In brazing, there is more control of the joins.
Conclusion
To choose a process whether soldering, brazing, or welding, scrutinize the application thoroughly. The type of metal or nonmetal materials, the intent, and the design of the joint, size of the structure decide to clinch the type of process. The key difference between the processes is the amount of heat used which decides according to the application.
Thank you for sparing your time to read this piece, now you put your opinion in the comment box to help us further.
Pick The Best Sources
https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/faqs/welding-brazing-and-soldering
https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-brazing-and-soldering
